In the biological realm, Darwin’s theory of natural selection posits that genetic diversity is a fundamental aspect of survival and adaptation. Diverse genetic traits can provide individuals with advantages in various environmental conditions, enhancing their ability to survive and reproduce. This principle of diversity is crucial not only in the natural world but also in human societies.
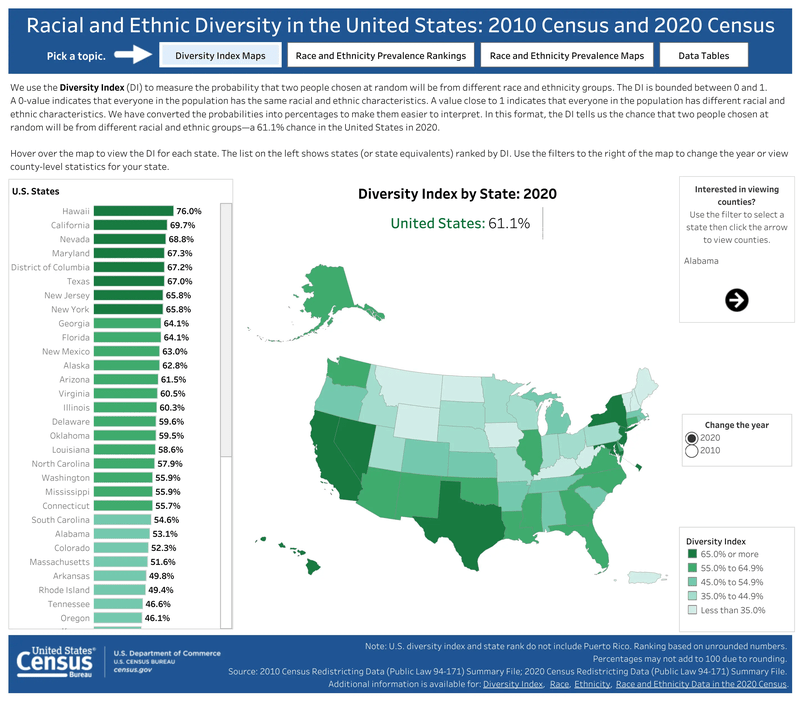
“Source: U.S. Census Bureau, Diversity Index by State: 2020, retrieved from https://www.census.gov/library/visualizations/interactive/racial-and-ethnic-diversity-in-the-united-states-2010-and-2020-census.html.”
As our world becomes more interconnected through advances in travel, technology, and communication, the historical barriers that once separated different ethnic and racial groups are increasingly blurred. This global interconnectivity has facilitated more frequent and deeper interactions among people from diverse backgrounds, leading naturally to more biracial and multiracial unions.
The rise in diverse relationships reflects a broader trend towards the appreciation of both biological and cultural diversity. Such relationships contribute to the genetic diversity of populations, which can enhance health and resilience against diseases. Furthermore, culturally, diversity enriches our communities by bringing different perspectives and experiences into the fold, fostering a more inclusive and adaptable society.
In this new era of globalization, the concept of racial identity itself is evolving. No longer seen as a fixed category, racial identity is becoming more fluid and complex. As individuals from different backgrounds create new familial bonds, the resulting diversity is a testament to the dynamic nature of human identities.
This ongoing evolution in how we perceive and experience racial identity not only mirrors the principles of natural selection but also underscores the societal shifts toward greater inclusivity and understanding. As we continue to embrace this diversity, it is imperative to recognize its value in strengthening both our biological heritage and our cultural fabric.
Historical Context of Racial Identities
Understanding the Past to Inform the Future
The construction and evolution of racial identities are deeply rooted in history, shaped by complex socio-economic and political dynamics. To understand the modern landscape of racial identity, it is essential to acknowledge how these identities have been influenced over centuries.
Historically, racial identities have often been constructed within the contexts of power and domination. For instance, during the colonial era, European powers delineated racial categories as a means of maintaining control over conquered peoples, often justifying exploitation with pseudo-scientific theories of racial superiority. These categories have had long-standing effects on societal structures and individual identities.
However, the historical narrative is also marked by the resilience and contributions of marginalized groups. Enslaved peoples in the Americas, for example, developed rich cultural traditions that have profoundly influenced national cultures in ways that are celebrated today. Their resilience in the face of brutal oppression is a testament to human spirit and creativity.
Insights from Experts
Scholars such as Howard Winant and Paul Gilroy have analyzed how racial categories were embedded in social and political institutions, highlighting that these constructs are not just reflections of physical differences but are deeply intertwined with historical power dynamics. Their insights help us see beyond simplistic explanations of race, revealing the layers of history that shape our present.
Acknowledging Complexity
The evolution of racial identities is influenced by myriad factors, including migration, economic changes, and global politics. As we have moved into a more interconnected world, these identities have become ever more complex and fluid. This complexity is crucial to understand: it helps prevent the reductive stereotyping that has historically fueled discrimination and misunderstanding.
Educational and Future-Oriented Perspective
This historical overview serves not only to educate but also to prepare us for future challenges. By understanding the roots of racial constructs, we can better address contemporary issues such as systemic racism and social inequality. It is through this lens of history that we can envision a more inclusive and equitable society.
Encouraging Dialogue
As we reflect on this history, it is vital to engage in dialogue about its impact on current racial issues and identities. This conversation is a stepping stone towards healing and progress. It encourages a collective examination of how far we have come and how far we still need to go in overcoming the legacies of our past.
Challenges and Controversies in Evolving Racial Identities
Navigating the Complexities of Identity
As racial identities evolve in an increasingly interconnected world, a myriad of challenges and controversies emerge, reflecting the complexities of this evolution. While the blending of cultures and races can enrich societies, it also raises significant issues that must be addressed to foster a genuinely inclusive environment.
Racial Discrimination and Systemic Inequities
Despite the progress in global interconnectivity and cultural exchange, racial discrimination persists as a profound challenge. Individuals from minority backgrounds often face systemic barriers in employment, education, and healthcare. These inequities are not relics of the past but active elements of modern societal structures, deeply embedded and often resistant to change. Addressing these issues requires not only policy reform but a societal shift in understanding and confronting racial prejudices.
Identity Politics and Social Fragmentation
The evolution of racial identities is sometimes accompanied by divisive identity politics, where race becomes a central point of political contention. These dynamics can lead to social fragmentation, as groups align along racial lines, sometimes at the expense of broader social solidarity. While identity politics can empower marginalized communities, they also pose the risk of entrenching divisions. This delicate balance requires careful navigation to ensure that advocacy for racial justice strengthens rather than divides.
The Biracial and Multiracial Experience
For biracial and multiracial individuals, the evolving concept of racial identity presents unique challenges. Navigating multiple cultural backgrounds often involves reconciling conflicting identities and dealing with societal pressures to ‘choose a side.’ The mainstream narrative around race can fail to accommodate the complex experiences of multiracial individuals, leading to feelings of isolation or identity conflict. Society’s growing recognition of these experiences is crucial in shaping a more inclusive understanding of racial identity.
Cultural Appropriation versus Appreciation
As cultures blend, the line between cultural appropriation and appreciation becomes increasingly blurred, leading to controversies over the use of cultural symbols and practices. When elements of a culture are adopted without a deep understanding of their significance or without respect for the originating culture, it can lead to accusations of appropriation. Promoting a more informed and respectful cultural exchange is essential to navigate this sensitive area.
Case Studies and Real-World Examples: Celebrating Diversity and Promoting Coexistence
Embracing Interethnic Unions as Ambassadors of Peace
In a world increasingly threatened by nuclear proliferation and geopolitical tensions, the importance of coexistence over domination cannot be overstated. A tangible manifestation of this coexistence is evident in the growing number of interethnic and interracial couples, many of whom share their lives on platforms like YouTube. These couples not only represent the merging of cultures but also act as potential ambassadors for peace, demonstrating daily that unity across racial and ethnic lines is not only possible but enriching.
Case Study: The Global Influence of Mixed Families
A noteworthy example is the increasing visibility of mixed-race families across various media. These families often share their experiences dealing with cultural differences and embracing diversity within their households. Their stories highlight how individual families are microcosms of larger societal integrations, providing a model for overcoming prejudices and fostering mutual respect and understanding.
The Role of Technology in Shaping Identities
Technology, especially social media, plays a pivotal role in shaping and broadcasting racial identities today. It allows for the celebration of diverse heritage and the challenging of traditional notions of race. Platforms like YouTube provide a stage for interracial couples and multicultural families to narrate their everyday lives, thus normalizing and promoting racial and cultural integration.
Historical Impact of Interracial Unions
Historically, interracial unions have served as benchmarks for racial progress in various societies. For instance, the legalization of interracial marriage in the United States with the 1967 Supreme Court decision in Loving v. Virginia marked a significant point of legal acknowledgment that race should not determine the bounds of personal relationships. The couple at the heart of this case, Richard and Mildred Loving, became symbols of racial harmony and legal change.
Multiracial Individuals in the Public Eye
Public figures who identify as multiracial also contribute to changing perceptions. For example, celebrities like Meghan Markle and Barack Obama have discussed their multiracial identities in ways that have influenced public discourse about race, identity, and belonging. Their presence in the public eye helps to challenge monolithic racial narratives and encourages a more nuanced understanding of identity that reflects the reality of many people’s lives.
Critical Perspectives: Understanding Racial Identities Through Power Dynamics
The Lens of Critical Race Theory
Critical Race Theory (CRT) provides a framework for examining racial identities that centers on the impact of systemic racism and the legacy of colonialism. This perspective emphasizes that race is not a biological fact but a social construct that has been instrumentalized to maintain power hierarchies. By incorporating CRT, we can explore how laws, cultural norms, and educational systems perpetuate racial disparities and how these can be dismantled.
Postcolonial Insights on Racial Identity
Postcolonial studies offer another critical lens, focusing on how colonial histories have shaped contemporary racial identities and power structures. This discipline examines the lasting impacts of colonial rule, including the arbitrary borders and racial classifications imposed by colonizers, which continue to affect political and social interactions today. By understanding these historical contexts, we can see how past power dynamics are entrenched in present-day racial issues, influencing everything from policy making to individual identity formation.
Power Dynamics in Everyday Interactions
Both CRT and postcolonial studies highlight how power dynamics play out in everyday interactions and institutional structures. For instance, in many Western societies, racial profiling by law enforcement, disparities in healthcare access, and inequalities in educational opportunities are manifestations of these power imbalances. Acknowledging these issues is crucial for fostering a more just society.
Deconstructing Racial Narratives
A critical approach involves questioning the dominant narratives around race that have been accepted as the norm. This includes challenging the myths of meritocracy and colorblindness that often obscure systemic inequalities. By deconstructing these narratives, we encourage a more honest dialogue about race, acknowledging the roles of privilege and systemic advantage.
Empowering Marginalized Voices
Critical perspectives emphasize the importance of elevating voices that have historically been marginalized. This not only helps in presenting a more accurate picture of racial dynamics but also in crafting policies and cultural norms that reflect the diverse experiences of all racial groups. It is about shifting the narrative to include those who have been excluded from the conversation.
Future Outlook: Emerging Trends and Scenarios in Racial Identity
The Intersection of Genetics and Racial Identity
Advancements in genetics and genomics are poised to dramatically alter our understanding of race. As we decode more about the human genome, the concept of race as a biological or genetic determinant is increasingly questioned. Research has repeatedly shown that genetic differences within so-called racial groups are often greater than differences between these groups. This scientific insight could lead to a broader societal recognition that race is largely a social construct, not a rigid biological reality. In the future, as genetic testing becomes more commonplace, our understanding of race could shift from a category that is imposed to one that is more fluid and complex, reflecting the true diversity within the human species.
Technology’s Role in Shaping Identity Perceptions
Technology, particularly through the use of social media and artificial intelligence, plays a crucial role in shaping our perceptions of identity. Algorithms used in everything from search engines to social media platforms can reinforce or challenge racial stereotypes, depending on how they are programmed. Increasing awareness of these biases and the implementation of more equitable AI practices could help promote a more inclusive representation of racial identities.
Moreover, virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technologies offer new ways for individuals to experience and empathize with the lives of people from different racial and ethnic backgrounds. These immersive technologies could become powerful tools in education and social activism, promoting a deeper understanding of the social constructs of race and the experiences of those affected by racial discrimination.
Globalization and the Fluidity of Racial Identities
As globalization continues, the interaction between diverse groups will likely increase, leading to more complex and fluid racial identities. This could result in a decrease in the significance of racial identities in favor of more nuanced, individualized understandings of self. The global mixing of cultures and races might lead to societies that are more racially and ethnically ambiguous, challenging the existing paradigms of race and identity.
The Political and Social Implications
The evolving understanding of racial identity will have significant political and social implications. As traditional racial categories become less relevant, there may be shifts in how policies around affirmative action, racial discrimination, and minority rights are approached. This will require careful navigation to ensure that the dismantling of outdated racial categories does not lead to the erasure of the historical and ongoing challenges faced by marginalized groups.
Conclusion
As we navigate the complexities of racial identity in a globalized world, we stand at a critical juncture that challenges us to embrace diversity not as a mere ideal but as a pivotal cornerstone of societal evolution. The convergence of diverse cultures and races enriches our collective human experience, encouraging us to rethink traditional boundaries and foster a more inclusive society. It is through understanding and valuing the myriad interactions among different racial and ethnic backgrounds that we can truly leverage the power of diversity to promote resilience and innovation in our interconnected world. By appreciating the dynamic and evolving nature of racial identities, we can create a future that acknowledges and celebrates diversity as a fundamental human asset.
Summary
This article explores the evolution of racial identity against the backdrop of Darwin’s principles of natural selection, illustrating how genetic diversity underpins not only survival and adaptation in the natural world but also enriches human societies. As globalization diminishes historical barriers, it fosters deeper interconnections that lead to an increase in biracial and multiracial unions, enhancing both genetic diversity and cultural richness. This shift towards a more fluid and complex understanding of racial identity reflects broader societal movements towards inclusivity and understanding. Embracing these changes, therefore, is crucial for fostering healthier populations and creating richer, more inclusive communities that align with both natural and social progress.


Leave a comment